The UAE’s corporate landscape has undergone a historic transformation with the introduction of Corporate Tax, formally enforced under Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022 and amended by Federal Decree-Law No. 60 of 2023. This landmark reform aligns the UAE with global taxation standards, strengthens economic transparency, and enhances the nation’s competitive edge in attracting foreign investment.
What is Corporate Tax?
Corporate Tax — also called Corporate Income Tax or Business Profits Tax—is a federal tax on the net profit of businesses operating in the UAE.
Who is eligible to pay Corporate Tax?
The following entities are eligible to pay corporate tax :
- Mainland companies – All juridical persons incorporated in the UAE.
- Free Zone companies – With special rules for Qualifying Free Zone Persons (QFZPs).
- Foreign entities that are effectively managed in the UAE, have a permanent establishment, or a taxable nexus.
- Natural Persons – Conducting business or professional activities with an annual UAE-sourced income exceeding AED 1 million.
Who Is Exempt?
The following entities are exempt from paying the ministry of finance corporate tax UAE:
- Government entities and wholly owned subsidiaries performing mandated activities.
- Qualifying public benefit entities (Cabinet Decision No. 37 of 2023)
- Qualifying investment funds meeting FTA criteria.
- Businesses engaged in natural resource extraction (subject to Emirate-level tax).
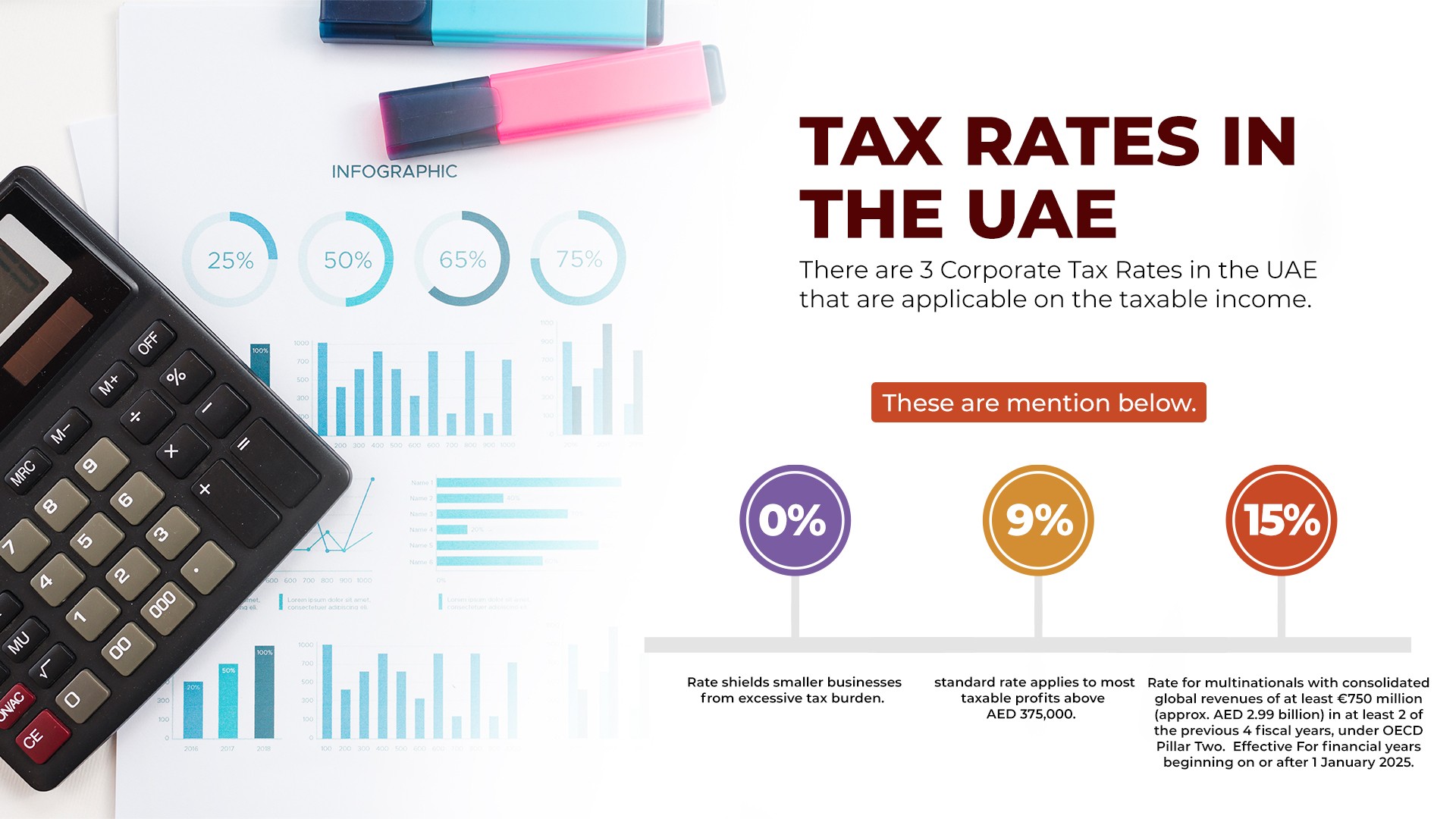
Tax Rates in the UAE (2025)
| Taxable Income | Rate |
|---|---|
| AED 0 – AED 375,000 | 0% |
| Above AED 375,000 | 9% |
| Multinational groups (> AED 3.15B revenue) | 15% |
Key points:
- 0% rate shields smaller businesses from excessive tax burden.
- 9% standard rate applies to most taxable profits above AED 375,000.
- 15% rate for multinationals with consolidated global revenues of at least €750 million (approx. AED 2.99 billion) in at least 2 of the previous 4 fiscal years, under OECD Pillar Two. Effective For financial years beginning on or after 1 January 2025.
Our Comprehensive Corporate Tax Services
We offer customized corporate tax solutions tailored to your specific business needs. Our corporate tax services include the following:

1. Corporate Tax Registration
- Timely Registration: Businesses must register through the FTA’s EmaraTax portal within 9 months from incorporation, or earlier if directed by the Authority.
- Who Must Register: Applies to mainland companies, free zone entities, and foreign businesses with a UAE taxable nexus.
- Expert Advisory: Guidance on permanent establishment status and its impact on your tax obligations.
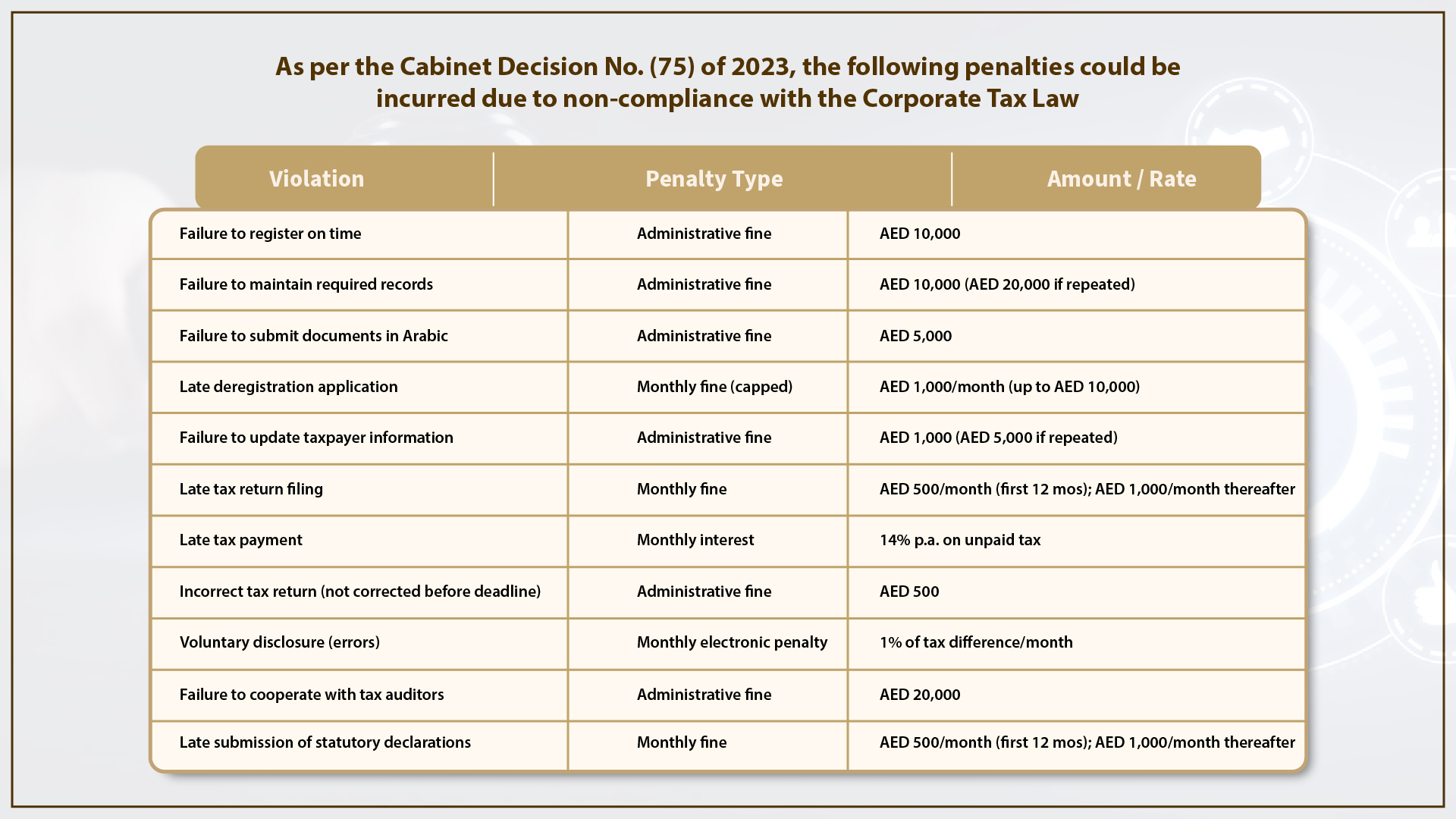
- Stay Compliant: Avoid hefty penalties — AED 10,000 fine for failure to register.
- Corporate Tax Deregistration
- Required when a business ceases all taxable activities, it is liquidated, or no longer falls under the scope of the Corporate Tax Law.
- Application for deregistration must be submitted via EmaraTax within 3 months from the cessation date.
- Failure to apply for deregistration: AED 1,000 per month (capped at AED 10,000).
2. Corporate Tax Return Filing Dubai
- Annual preparation & submission of corporate tax return within 12 months of the financial year end.
- Accurate income and expense reporting per IFRS.
- Handling of complex adjustments: unrealized gains, exempt income, related party transactions.
Note: Late filing penalties from AED 500 to AED 1,000/month.
3. Corporate Tax Audit
- Pre-audit compliance reviews.
- Conducted in line with FTA-approved audit standards. The FTA can audit and reassess tax returns for up to 5 years from the end of the relevant tax period (extended to 7 years in cases of tax evasion or failure to register), as per Article 50 of Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022 on the Taxation of Corporations and Businesses.
- Verification of taxable income, allowable deductions, and exemptions.
4. Free Zone Corporate Tax Advisory Services
- QFZP qualification assessment.
- Income Monitoring: Ongoing review of non-qualifying income to ensure it remains within the de minimis thresholds.
- Proactive Advisory: Strategic planning of activities to maintain Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP) status and safeguard the 0% tax rate.
- Risk Mitigation: Early identification of potential breaches to avoid losing preferential tax treatment.
- If non-qualifying income exceeds the lower of 5% of total revenue or AED 5 million, the Free Zone entity loses Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP) status and becomes fully subject to the 9% Corporate Tax.
- Guidance on permitted qualifying activities under ministerial decisions.
5. Transfer Pricing Compliance
- Preparation of Master File and Local File in line with OECD guidelines.
- Related party transaction documentation.
- Advance pricing arrangement advice.
- Prevention of profit shifting disputes.
- The Transfer Pricing documentation is required if the business has:
- Consolidated group revenue ≥ AED 3.15 billion, or
- Revenue ≥ AED 200 million and cross-border related-party transactions, as per the Ministerial Decision No. 97 of 2023 on the Requirements for Maintaining Transfer Pricing Documentation.
6. Exemption & Relief Advisory
- Small Business Relief applications.
- Participation Exemption for qualifying shareholdings.
- At least 5% ownership interest in the subsidiary.
- Held continuously for at least 12 months (or intention to hold for 12 months).
- Subsidiary must be subject to tax at a rate of at least 9% (or equivalent foreign tax rate), as per Articles 23 & 24 of Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022.
- Public Benefit Entity exemption processing.
- Guidance for pension funds, government entities, and qualifying investment funds.
7. Corporate Tax Accounting
- IFRS-compliant financial statement preparation.
- Periodic tax liability assessment.
- Record-keeping systems aligned with FTA requirements (minimum 7 years).
- Integration with your ERP or accounting software.
- Penalty: Failure to maintain records could lead to AED 10,000 per violation, rising to AED 20,000 if repeated within 24 months, as per Cabinet Decision No. 75 of 2023 on Administrative Penalties for Corporate Tax.
Corporate Tax Service Comparison Table
| Feature | Mainland Company | Free Zone Company (QFZP) | Offshore Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applicable Tax Rate | 0% up to AED 375,000; 9% above | 0% on qualifying income; 9% on taxable income | Generally exempt in UAE, provided there is no UAE sourced income (but may be taxable in foreign jurisdiction) |
| Qualifying Criteria | All mainland-licensed businesses | Ensure full adherence to requirements for Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP) status — including adequate substance in the UAE, conducting qualifying activities, maintaining audited financial statements, and monitoring non-qualifying income (must not exceed 5% of total income or AED 5 million, whichever is lower). | Must be incorporated in an offshore jurisdiction approved by UAE authorities |
| Scope of Activities | Can operate anywhere in UAE and globally | Primarily within Free Zone and internationally; limited mainland dealings (taxable at 9%) | Cannot conduct business within UAE mainland; can hold assets, investments, and operate internationally |
| Audit Requirement | Mandatory if meeting turnover thresholds or as per FTA demand | Mandatory audited financial statements for QFZP status | Usually no UAE audit requirement unless opening UAE bank account |
| Registration with FTA |
Mandatory for all taxable persons.
Penalty for Non-Compliance: AED 10,000 (AED 20,000 if repeated within 24 months). |
Mandatory for all taxable persons, even at 0%.
Penalty for Non-Compliance: AED 10,000 (AED 20,000 if repeated). |
Not required unless generating UAE-source income |
| Key Advantages | Full market access, clear tax rules | 0% tax benefit, strategic locations, modern infrastructure | Asset protection, privacy, zero UAE tax if no local income |
| Key Disadvantages | Subject to standard 9% tax above threshold | QFZP status is retained only if the entity consistently meets FTA requirements on substance, qualifying activities, audited financials, and de minimis income limits. Risk of Disqualification: Failure to meet these conditions can result in the loss of QFZP status for a period of 5 years, leading to the withdrawal of the 0% tax benefit. | Limited UAE operational scope, banking restrictions |
| Best For | Local businesses serving UAE mainland customers | Export-oriented firms, service providers, regional HQs | Holding companies, international trading, asset protection |
Necessary Documents for Corporate Tax Registration
The following documents are required for Corporate Tax Registration purposes:
1. For Natural Persons:
- Trade license (where applicable)
- Emirates ID or passport of the applicant
2. For Legal Persons:
- Trade license
- Emirates ID or passport of the authorized signatory
- Proof of authorization for the authorized signatory (e.g., Power of Attorney or Memorandum of Association)
Essential Documents for Filing Corporate Tax Return
The following documents are necessary to file corporation tax return :
- Trade License & Tax Registration.
- Financial Statements.
- General Ledger & Bank Statements.
- Invoices, Receipts & Expense Records.
- Fixed Asset Register & Depreciation Schedules.
- VAT Records (if applicable).
- Transfer Pricing Documentation
- Supporting Schedules & Adjustments
- Corporate Tax Registration Certificate
- Additional Attachments (as applicable)
- Legal Documents & IDs
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Corporate Tax Deadlines
Corporate Tax Registration Deadlines
1. Entities Incorporated on or After 1 March 2024
- Deadline: Must register within three months of the date of incorporation.
2. Natural Persons (Individuals)
- Deadline: Must register by 31 March following the year in which their UAE business turnover exceeded AED 1 million.
- Example: If turnover crossed AED 1M by 31 July 2024, registration is due by 31 March 2025, and the tax return must be submitted by 30 September 2025.
3. Penalty Waiver Opportunity
- What’s at stake: If you missed the registration deadline, a penalty waiver may still be granted if the first tax return—or annual exemption declaration—is filed within seven months after the end of your first tax period.
- Example: For most companies with a 2024 tax year, filing by 31 July 2025 could render the AED 10,000 penalty void or refunded.
Corporate Tax Return Filing Deadlines
Standard Filing Timeline
- General Rule: Corporate Tax Returns and payments are due within nine months from the end of your tax period.
- If your fiscal year ended 31 December 2024, your filing deadline is 30 September 2025.
Corporate Tax Rules in the UAE Free Zones
- Qualifying Free Zone Persons (QFZPs) enjoy 0% FTA corporate tax on qualifying income if they meet:
- Adequate substance in the UAE
- Income from qualifying activities
- Non-qualifying income ≤ 5% of total revenue or AED 5 million (whichever is lower)
- Audited financial statements submitted to FTA
- Opting for Small Business Relief disqualifies you from QFZP benefits for 5 years.
Latest UAE Corporate Tax Law Highlights (2025)
1. New Cabinet Decisions & FTA Regulations
- Cabinet Decision No. 55 of 2025 (CD 55): Extends corporate tax exemption to foreign-incorporated entities that are entirely owned and controlled by exempt persons (e.g., government or public funds), retroactive to June 1, 2023.
- Cabinet Decision No. 63 of 2025 (CD 63): Rules that unincorporated partnerships can be treated as standalone taxable persons under the UAE Corporate Tax Law, also with retrospective effect from June 1, 2023.
- FTA Decision No. 5 of 2025: Sets out tax compliance obligations for unincorporated partnerships, foreign partnerships, and family foundations. This comes into effect July 1, 2025.
2. Introducing the Domestic Minimum Top-Up Tax (DMTT)
- Effective from January 1, 2025, or later, the UAE is implementing the Domestic Minimum Top-Up Tax (DMTT) .
- This meets the OECD's Pillar Two rules to offer a 15% effective tax rate on large multinational enterprises (MNEs).
- Applies to MNEs with €750 million (approx. AED 2.99 billion) or more in consolidated global revenue, in at least 2 of the past 4 years.
- This ensures the UAE does not lose tax collection if foreign jurisdictions impose a top-up, preserving the UAE's tax base.
3. Expanded Corporate Tax Exemptions
- Recent updates ensure equal tax treatment for foreign and domestic exempt entities. If certain foreign-owned entities meet ownership and activity criteria, they too qualify for exemption ("exempt under Article 4(1) of the CT law")—effective retroactively to June 1, 2023.
4. Free Zone Entities & Substance Requirements
- Qualifying Free Zone Persons (QFZPs) continue to benefit from 0% corporate tax on qualifying income, provided they meet strict criteria regarding substance, qualifying activities, and maintaining audited financials.
- Registration is mandatory, regardless of tax rate status—non-registration attracts penalties.
- Opting for Small Business Relief (for revenue ≤ AED 3 million) means forfeiting QFZP status and the 0% rate for the current and following 4 years.
5. Key Compliance Deadlines & Requirements
- Businesses must register and file corporate tax for tax periods starting June 1, 2023.
- The deadline for tax registration for individuals earning over AED 1 million through business: March 31, 2025.
- For audits, transfer pricing documentation, and filings, the key compliance window is September 30, 2025.
- Dubai's Executive Council Decision No. 11/2025 allows free zone companies to expand into mainland Dubai (excluding DIFC entities), subject to licensing from the Department of Economy and Tourism.
Corporate Tax Updates – 2025 – Summary Table
| Update / Change | Effective Date | Who’s Affected | Key Details | Compliance Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business Relief (SBR) Extension | Extended until Dec 31, 2026 | UAE businesses with ≤ AED 3M annual revenue | Businesses can elect to be treated as having no taxable income for the period. | Review annual revenue; apply for SBR via FTA if eligible; maintain records to prove eligibility. |
| Free Zone Qualifying Income Clarifications | Effective May 2024 | Qualifying Free Zone Persons (QFZPs) | Non-qualifying income must not exceed 5% of total revenue or AED 5M (whichever is lower). Breach removes QFZP status for 5 years. | Maintain separate accounts for qualifying/non-qualifying income; monitor income mix monthly. |
| Natural Persons Corporate Tax Registration | From 2024 onwards | Individuals with UAE-sourced business income > AED 1M/year | Applies to freelancers, sole proprietors, real estate brokers, etc. | Track annual business income; register via EmaraTax; keep business records in line with FTA requirements. |
| New Penalty Regime | Effective 2024 | All corporate tax-registered businesses and individuals | AED 10K for non-registration; AED 500–1,000/month late filing 15% fixed + 1% monthly for late disclosure; AED 5K for not providing Arabic documents. | Maintain a tax deadline calendar; prepare bilingual (English/Arabic) financial documentation. |
| OECD Pillar Two – 15% Minimum Tax | From 2025 | Multinationals with global revenues > AED 3.15B | 15% minimum effective tax rate on adjusted profits per OECD rules. | Prepare OECD-compliant transfer pricing files; assess global effective tax rate annually; adjust structures if needed. |
Corporate Tax Accounting
Corporate Tax Accounting refers to the process of recording, classifying, and reporting business transactions in accordance with the UAE Corporate Tax Law, IFRS, and FTA requirements.
Key Requirements for Corporate Tax Accounting
-
Accounting Standards:
All taxable persons must prepare financial statements based on IFRS or IFRS for SMEs (for smaller businesses).
-
Record-Keeping Obligations:
Companies must maintain accurate records for at least 7 years after the end of the relevant tax period.
-
Books of Accounts:
Businesses are required to maintain proper books including:
- General ledger and trial balance
- Profit & loss account and balance sheet
- Cash flow statements
- Bank reconciliations
- Accounts receivable/payable records
-
Adjustments for Tax Purposes:
Certain accounting profits may be adjusted for tax computation, e.g.:
- Exempt income (dividends, certain capital gains)
- Disallowed expenses (fines, donations not approved)
- Reliefs and deductions (foreign tax credits, small business relief)
Why Proper Tax Accounting Matters
- Calculating Corporation Tax Liability: Ensures businesses pay only what is legally required.
- Audit Readiness: Strong accounting records form the foundation for successful tax audits.
- Penalty Avoidance: Incomplete or inaccurate accounting may result in fines (AED 10,000+ for non-compliance).
- Strategic Planning: Well-structured tax accounting allows for planning around deductions, group reliefs, and incentives.
Corporate Tax Audit
A Corporate Tax Audit is an official inspection carried out by the FTA to verify whether a company has complied with Corporate Tax laws and correctly calculated and reported its tax obligations.
How FTA Conducts a Tax Audit
The FTA issues prior notice to the business, though in some cases, audits may be conducted with little warning.
- The audit can cover:
- Corporate tax returns
- Supporting financial statements
- Bank transactions
- Invoices and contracts
- Transfer pricing documentation
- On-site / Off-site Audits: Audits may take place at the taxpayer’s premises or at the FTA’s offices.
- Language Requirement: Businesses must be able to provide documents in Arabic when requested. Failure to do so may result in penalties (AED 5,000 per instance).
Essential Criteria for FTA Audits
The FTA may select businesses for audit based on:
- Significant discrepancies between accounting income and taxable income.
- Unusually high deductions or exemptions claimed.
- Frequent losses or revenue inconsistencies.
- Non-compliance in VAT or Excise filings (cross-checked by FTA systems).
- Random sampling as part of compliance enforcement.
Documents Required During Tax Audit
- Tax return copies and acknowledgments.
- Audited financial statements.
- Detailed ledgers, invoices, and receipts.
- Transfer pricing reports for related-party transactions.
- Contracts, loan agreements, and intercompany arrangements.
- Proof of tax payments.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to maintain proper accounting or comply during a tax audit can lead to:
- AED 10,000 fine for failure to register for Corporate Tax.
- AED 500–1,000 per month for late filing of tax returns.
- AED 5,000 fine for failure to submit records in Arabic.
- Additional penalties for under-reporting taxable income, misstatements, or fraudulent reporting.
Best Practices for Businesses
To ensure smooth Corporate Tax Accounting and Audit compliance:
- Engage FTA-Approved Tax Auditors: Only recognized auditors can provide credibility and audit-readiness.
- Automate Accounting Systems: Use ERP or cloud-based accounting software for real-time compliance.
- Conduct Internal Tax Health Checks: Proactive reviews to identify gaps before an FTA audit.
- Document Transfer Pricing Policies: Especially for free zone and multinational groups.
- Maintain Bilingual Records: Prepare English and Arabic versions to avoid translation delays during audits.
Why Choose AMCA as Your Corporate Tax Auditor?

1. FTA-Approved Tax Auditor – A Mark of Trust & Authority
Our status as an FTA-Approved Tax Auditor is an official recognition of our capability, professionalism, and adherence to the highest auditing and tax standards in the UAE.
- Directly recognized by the Federal Tax Authority.
- Demonstrated compliance with strict professional criteria, ethics, and qualifications.
- Ensures our audit opinions and compliance checks carry the weight of authority during FTA reviews or disputes.
2. Expertise Across Mainland, Free Zone, and Multinational Taxation
The UAE’s tax environment varies significantly across business zones and structures. Our team has decades of combined experience navigating these complexities.
- Mainland businesses – Applying standard tax rates, exemptions, and compliance obligations.
- Free Zone entities – Advising on QFZP requirements, qualifying income, and structuring to preserve the 0% rate.
- Multinational Enterprises (MNEs) – Ensuring compliance with OECD Pillar Two, transfer pricing regulations, and global tax alignment.
3. Industry-Specific Advisory for Tailored Solutions
We understand that tax challenges differ depending on your industry and operating model.
- Hospitality & Tourism – Seasonal income structuring and asset depreciation strategies.
- Real Estate & Construction – Treatment of long-term contracts, WIP (Work in Progress), and project-based revenue recognition.
- Technology & Startups – Leveraging small business relief, R&D deductions, and IP management.
- Retail & E-commerce – Managing cross-border supply chains, VAT implications, and intercompany transactions.
4. Proactive Compliance Monitoring to Avoid Penalties
Penalties in the UAE for corporate tax non-compliance can be substantial. We take a proactive, year-round approach to protect your business.
- Continuous compliance tracking against FTA deadlines.
- Early identification of risks, from improper expense classification to related party transaction issues.
- Internal compliance health checks to prevent late filings, underpayments, or inaccurate disclosures.
5. Strategic Structuring for Long-Term Tax Efficiency
Corporate Tax compliance Dubai is not just about meeting deadlines—it’s also about positioning your business for sustainable growth.
- Business structure optimization for reduced tax exposure.
- Intercompany transaction planning for global tax alignment.
- Leveraging allowable deductions, exemptions, and relief schemes.
- Planning for changes in UAE tax law and international agreements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What happens if I miss my corporate tax registration deadline?
A: The FTA imposes an AED 10,000 penalty for late registration, doubling to AED 20,000 for repeat violations within 24 months.
Q2: Can Free Zone companies still benefit from 0% tax in 2025?
A: Yes, Free Zone companies in the UAE can continue to benefit from the 0% corporate tax rate in 2025, provided they qualify as a Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP). This status is governed by Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022 on Corporate Tax, specifically under Article 18, and is further detailed in Ministerial Decision No. 229 of 2025, which refines the scope of Qualifying and Excluded Activities for Free Zone entities. Meet the FTA’s Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP) conditions, such as:
- Maintaining adequate substance in the UAE
- Carrying out qualifying activities
- Preparing and submitting audited financial statements
- Ensuring non-qualifying income does not exceed 5% of total revenue or AED 5 million (whichever is lower)
If these criteria were not violated in the previous tax period, the company remains eligible for the 0% rate in 2025.
Q3: How is taxable income calculated?
A: Based on accounting net profit/loss per IFRS, adjusted for exempt income, related-party transactions, and other FTA-prescribed adjustments.
Q4: Are natural persons taxed?
A: Yes, if their UAE business income exceeds AED 1 million annually.
Q5: What is Small Business Relief, and how do I claim it?
A: To qualify for Small Business Relief, a resident taxable person (either a natural or juridical person) must meet the following conditions:
- Revenue Threshold: The total revenue must not exceed AED 3 million for the relevant tax period and all previous tax periods.
- Election Requirement: The relief must be elected for each tax period by notifying the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) through the tax return for the respective period.
- Business Type Restrictions:
- The entity must not be a Qualifying Free Zone Person.
- The entity must not be a member of a multinational group with consolidated group revenue exceeding AED 3.15 billion.
Q6: How to register for corporate tax Dubai?
A: To register for corporate tax in Dubai, businesses must apply through the FTA portal.
Stay Compliant with AMCA Auditing
AMCA Auditing, a corporate tax consultant firm, ensures that your filings are accurate, timely, and optimized for your business goals. Let’s safeguard your compliance and maximize your tax efficiency today!
Federal Decree-Law No. (47) of 2022 on the Taxation of Corporations and Businesses

